The universe thrives on an intricate dance of forces, where the masses of objects and the distances separating them play pivotal roles in shaping the cosmos as we know it. The gravitational pull between objects is fundamentally determined by their masses and the distance that separates them. This relationship not only influences celestial bodies but also has real-world implications that we experience daily. Understanding how these two factors interact can unlock the mysteries of gravity and provide insights into the broader universe.
As we delve deeper into the mechanics of gravity, we are compelled to ask ourselves: What defines the masses of various objects, and how does increasing the distance between them affect their gravitational attraction? This exploration leads us to a fascinating journey through physics, where concepts such as mass, distance, and gravitational force intertwine. Our everyday experiences with gravity may seem mundane, yet they are rooted in profound scientific principles that govern the very fabric of our reality.
In this article, we will examine the nuances of how masses of objects and increasing the distance between the objects influence gravitational forces. We will explore theoretical foundations, practical applications, and even engage with some thought-provoking questions that challenge our understanding. So, join us as we unravel the complexities of gravity, mass, and distance—elements that hold the key to not only understanding our planet but also the universe beyond.
What is the Relationship Between Mass and Gravity?
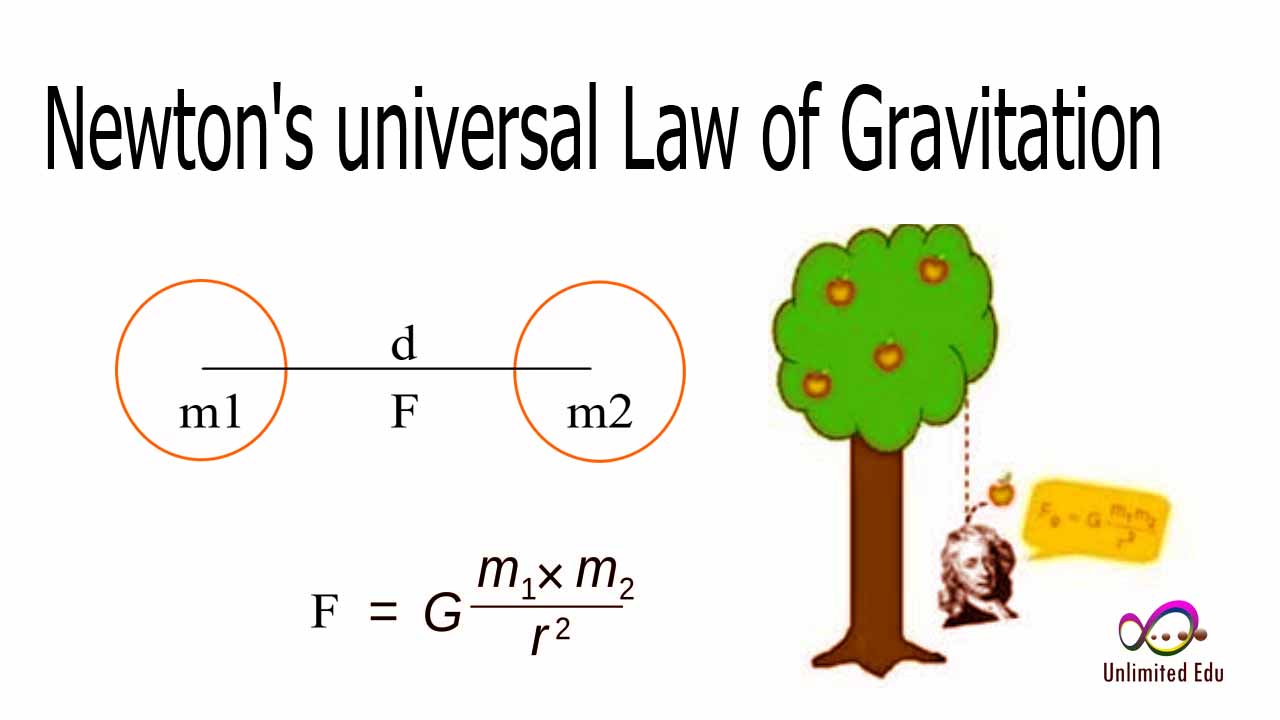
The relationship between mass and gravity is fundamental to understanding how objects interact with one another in the universe. Gravity is the force that pulls two masses toward each other, and its strength depends on two main factors: the masses of the objects involved and the distance between them. According to Newton's law of universal gravitation, the force of gravity can be calculated using the formula:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
Where:
- F = gravitational force
- G = gravitational constant
- m1 and m2 = masses of the two objects
- r = distance between the centers of the two objects
This formula illustrates that the gravitational force increases with greater mass and decreases with greater distance. Therefore, larger objects exert a stronger gravitational pull, while increasing the distance between them weakens this force.
How Do Masses of Objects Affect Gravitational Force?
The masses of objects significantly impact the gravitational force they exert on each other. For instance, the Earth, being a massive body, exerts a considerable gravitational pull on objects on its surface. This pull is what keeps us grounded and is responsible for the phenomenon of weight. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull. This principle is evident in various celestial bodies, such as stars and planets, where their immense mass generates gravitational fields that influence other bodies in their vicinity.
Can We Observe the Effects of Mass on Gravity in Everyday Life?
Absolutely! Everyday experiences provide tangible examples of the effects of mass on gravity. Consider the following scenarios:
- Dropping two objects of different masses from the same height shows that they hit the ground simultaneously, demonstrating that gravity acts uniformly regardless of mass.
- The varying weights of different objects, such as a bowling ball versus a feather, can be attributed to their mass and the gravitational pull exerted by the Earth.
- The phenomenon of tides on Earth is influenced by the mass of the moon and its distance from our planet, showcasing the interplay between gravitational forces and mass.
What Happens When We Increase the Distance Between Two Objects?
Increasing the distance between two objects significantly impacts the gravitational force acting between them. As mentioned earlier, the gravitational force diminishes with distance according to the inverse square law. This means that as objects move farther apart, the force of attraction between them decreases rapidly.
How Does Distance Impact Gravitational Pull?
The effect of distance on gravitational pull can be observed in various scenarios:
- In space, planets orbiting the sun experience varying gravitational forces depending on their distance from the sun. For example, Earth is at an optimal distance that allows for a stable orbit, while other planets experience different gravitational influences due to their distances.
- The concept of escape velocity is directly related to distance; the farther an object is from a massive body, the less force is required to escape its gravitational pull.
- Satellite communications also rely on the distance between satellites and Earth; as satellites move further away, the strength of the signal received diminishes.
What Are the Implications of Increasing Distance on Celestial Bodies?
In the cosmic realm, increasing distances can lead to fascinating consequences:
- Galaxies moving away from each other exhibit redshift, a phenomenon that occurs due to the expanding universe and increasing distances.
- Black holes exert an immense gravitational pull, but as you increase distance from them, the gravitational effects become negligible, allowing for stable orbits of surrounding celestial bodies.
- The concepts of gravitational waves and their detection underscore the importance of understanding mass and distance, as these waves are ripples in spacetime caused by the acceleration of massive objects.
How Can We Calculate Gravitational Forces Between Objects?
Calculating gravitational forces requires understanding the masses of the objects involved and their distance. Using Newton's law of gravitation mentioned earlier, we can determine the force of attraction between any two masses. However, for more complex systems involving multiple objects, advanced calculations may be necessary.
What Tools and Methods Are Used for Gravitational Calculations?
Several tools and methods can assist in calculating gravitational forces:
- Mathematical modeling and simulations are often used in astrophysics to predict gravitational interactions between celestial bodies.
- Software programs can calculate gravitational forces in complex systems, taking into account multiple variables and factors.
- Experimental methods, such as pendulum experiments, can provide empirical data to validate theoretical calculations.
How Important Is Understanding Mass and Distance in Space Exploration?
Understanding the masses of objects and the distances between them is crucial for successful space exploration. Missions to other planets, moons, and celestial bodies require precise calculations of gravitational forces to ensure safe landings, stable orbits, and efficient fuel usage. As we continue to explore the cosmos, our comprehension of these concepts will guide us in navigating the vastness of space and unlocking its secrets.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Masses and Distance in the Universe
In conclusion, the masses of the objects and increasing the distance between the objects are fundamental concepts that shape our understanding of gravity and its effects on the universe. Whether it's the pull of gravity keeping us grounded on Earth or the complex gravitational interactions governing celestial bodies, these principles are interwoven into the very fabric of our existence. By delving into the dynamics between mass and distance, we gain insights that extend beyond our planet, offering a glimpse into the cosmos and the forces that govern it.